Category
In the contemporary landscape of global connectivity, the Internet stands as a transformative force that has reshaped every facet of human interaction, communication, and commerce. From its humble origins to its pervasive presence in our daily lives, the Internet has evolved into an essential infrastructure that underpins modern society. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the foundational principles of the Internet, delving into its history, infrastructure, operational mechanisms, key technologies, security considerations, societal impacts, and future trends.
The Internet\'s journey began in the 1960s as a decentralized network called ARPANET, developed by the United States Department of Defense. Originally designed to ensure robust communication in the event of a nuclear attack, ARPANET laid the groundwork for a revolutionary concept: a network that could connect computers and enable information exchange across vast distances. Over subsequent decades, the Internet expanded beyond its military and academic origins, embracing commercial applications and eventually becoming a global phenomenon.
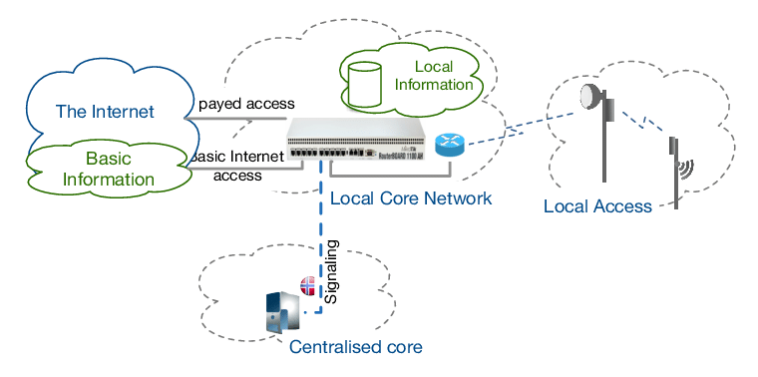
At its core, the Internet relies on a complex infrastructure composed of diverse components that work in tandem to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange.

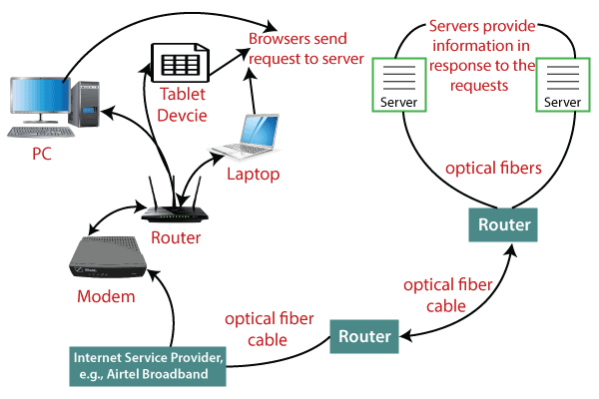
Network Components and Architecture: The Internet operates on a decentralized architecture, comprising interconnected networks of computers, servers, routers, and switches. Servers play a pivotal role in hosting data and services accessible to users worldwide, while clients, such as personal computers and mobile devices, access these services through web browsers and applications.
Protocols and Data Transmission: Key protocols like TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) govern how data is transmitted across the Internet. Data is packetized into small units before being transmitted, ensuring efficient delivery and error detection through mechanisms like packet-switching and routing.
Fiber Optics and Data Centers: Fiber optic cables form the backbone of Internet infrastructure, enabling high-speed transmission of data through the use of light pulses. Data centers, large facilities equipped with servers and networking equipment, store and distribute vast amounts of digital information to users globally. These centers are strategically located to optimize speed, reliability, and accessibility of online content and services.
The Internet operates on a fundamental principle of decentralized communication and information retrieval, enabling users to access a wealth of resources and services with ease.
Domain Name System (DNS): The DNS serves as the Internet\'s address book, translating human-readable domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into numerical IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1) that computers use to identify and communicate with each other. This translation process ensures seamless navigation and accessibility of websites and online resources.
World Wide Web (WWW): The WWW, pioneered by Tim Berners-Lee in the late 1980s, revolutionized how information is accessed and shared online. It operates on protocols like HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and its secure variant HTTPS, facilitating the transfer of web pages, documents, and multimedia content between web servers and clients. Web browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari provide users with intuitive interfaces to navigate the Web and interact with digital content effortlessly.
Beyond basic web browsing, the Internet encompasses a myriad of technologies and applications that enhance connectivity, collaboration, and innovation across various domains.
Email and Instant Messaging: Email, powered by protocols like SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol), enables users to send and receive messages electronically. Instant messaging platforms such as WhatsApp and Slack facilitate real-time communication and collaboration, connecting individuals and groups globally.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals store, access, and manage data and applications online. It encompasses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) models, providing scalable and cost-effective solutions for computing resources, storage, and software deployment.
As the Internet continues to evolve, ensuring cybersecurity and protecting user privacy have become paramount concerns for individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide.
Cybersecurity Threats: Malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches pose significant risks to Internet users\' security and data integrity. Antivirus software, firewalls, and regular system updates are essential safeguards against these threats, mitigating vulnerabilities and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Encryption and Secure Communication: Technologies like SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encrypt data transmitted over the Internet, ensuring confidentiality and preventing interception by malicious actors. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) establish secure connections between users and private networks, enhancing privacy and anonymity while browsing online.
The Internet\'s pervasive influence extends beyond technological advancements, shaping social dynamics, economic landscapes, and cultural paradigms on a global scale.
Global Connectivity: Despite efforts to bridge the digital divide, disparities in Internet access persist across regions and demographics, influencing educational opportunities, economic development, and social inclusion. E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Alibaba have democratized commerce, enabling businesses of all sizes to reach global markets and consumers to access a diverse array of products and services.
Social Media and Digital Interaction: Social networking platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have redefined how individuals connect, communicate, and share information online. These platforms facilitate real-time interaction, community engagement, and cultural exchange, fostering virtual communities and amplifying voices across geographical boundaries.
Looking ahead, emerging technologies and trends are poised to further transform the Internet landscape, driving innovation, efficiency, and connectivity across industries and sectors.
5G and Next-Generation Networks: Fifth-generation (5G) wireless technology promises enhanced speed, lower latency, and greater bandwidth, supporting advanced applications like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and autonomous vehicles. These advancements will revolutionize mobile connectivity, IoT (Internet of Things) deployments, and industrial automation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data: AI algorithms and machine learning techniques are transforming data analysis, predictive modeling, and decision-making processes across diverse domains. Big data analytics harnesses vast datasets to extract actionable insights, optimize operational efficiency, and drive innovation in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
In conclusion, the Internet remains an ever-evolving ecosystem that continues to shape our interconnected world profoundly. From its inception as a military and academic network to its ubiquitous presence in our personal and professional lives, the Internet exemplifies humanity\'s ingenuity and resilience in harnessing technology to foster communication, collaboration, and progress. By understanding the foundational principles and technologies underpinning the Internet, users can navigate its complexities responsibly and leverage its vast potential to innovate, connect, and thrive in the digital age. As we embark on future advancements and innovations, the Internet\'s role as a catalyst for global connectivity and socioeconomic development will undoubtedly continue to evolve, shaping the contours of our interconnected future.